The Distance Formula
We will use the Pythagorean Theorem to find a formula we can use to
find the distance between two points in the xy-plane.
Consider any two points in the xy-plane. Let’s label them P1(x1, y1) and
P2(x2, y2).
We draw a right triangle with P1 and P2 as the ends of the hypotenuse.
The length of the horizontal side of the triangle is the run from P1 to P2.
That run is | x2 - x1 |. We use absolute value because the length cannot be
negative.
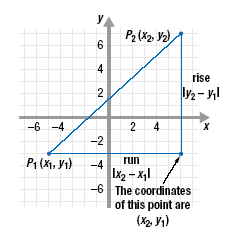
Likewise, the length of the vertical side of the triangle is the rise between
P1 and P2. That rise is | y2 - y1 |.
| In the Pythagorean Theorem:
Substitute the run, | x2 - x1 |, for a.
Substitute the rise, | y2 - y1 |, for b.
When we square a quantity, we get a positive number. So we do not need
the absolute value symbols. We replace them with parentheses.
|
c2 = a2 + b2
c2 = | x2 - x1 |2 + | y2
- y1 |2
c2 = (x2 - x1)2 + (y2
- y1)2 |
|
To find c, we take the square root.
We call this result the distance formula. |
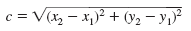 |
Formula — The Distance Formula
Let P1(x1, y1) and P2(x2, y2) represent any two points in the xy-plane.
The distance, d, between P1 and P2 is given by
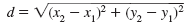
Example 1
Use the distance formula to find the distance between the points (5, 0) and
(-2, -8).
Solution
| Let (x1, y1) be (5, 0) and (x2, y2) be
(-2, -8). |
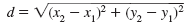 |
| Substitute these values into the
distance formula. |
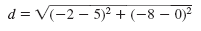 |
| Simplify. |
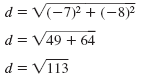 |
The distance, d, is
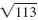 units. units.
Note:
We obtain the same answer if we use (5, 0)
for (x2, y2) and (-2, -8) for (x1, y1).
|